Which Part Of The Ip Address Does The Router Use To Determine Where To Send Data Packets
Previously, we looked at a simplified IP parcel, with fields for the source and destination addresses equally well as the information it transports.
Previously, we looked at a simplified IP packet, with fields for the source and destination addresses as well as the data it transports. In a real IP bundle header there are several other fields.
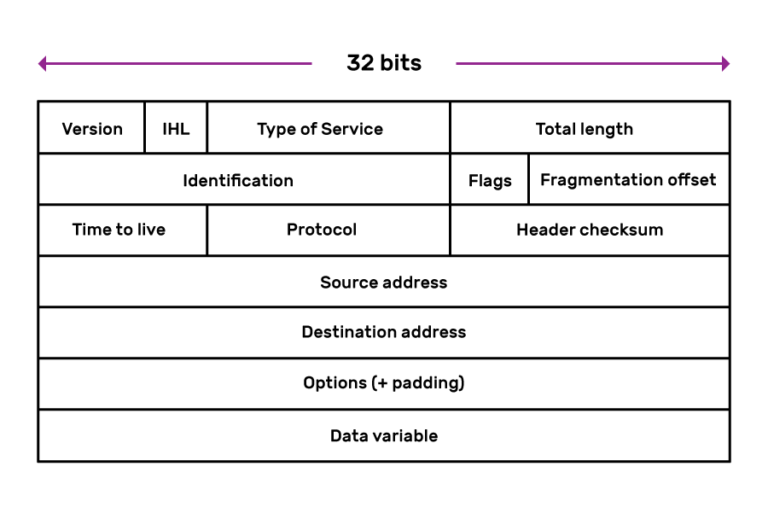
- IHL indicates the header length.
- Packets apply Blazon of Service to request special handling (e.thou. being put at the forepart of whatsoever queues).
- The identification, flags, and fragmentation offset fields go along rails of each fragment when an IP package is split upward into smaller packets.
- The time to live is set when the IP packet is sent off, and the number is reduced by 1 each fourth dimension the packet goes through a router. When the time to live gets to 0, the bundle is deleted. This stops packets from circulating in a loop.
You tin can observe all the details about the header of IPv4 packets as well as the header of IPv6 packets on Wikipedia.
Routers and routing
Routers got their name considering they route IP Packets across networks: a router device connects different links. It examines IP package headers, looking at the destination address and consulting a routing table of known networks. The table indicates which connections to transport the packet on every bit the side by side link. The connections on a router are called interfaces: through the router, they interface between different link types.
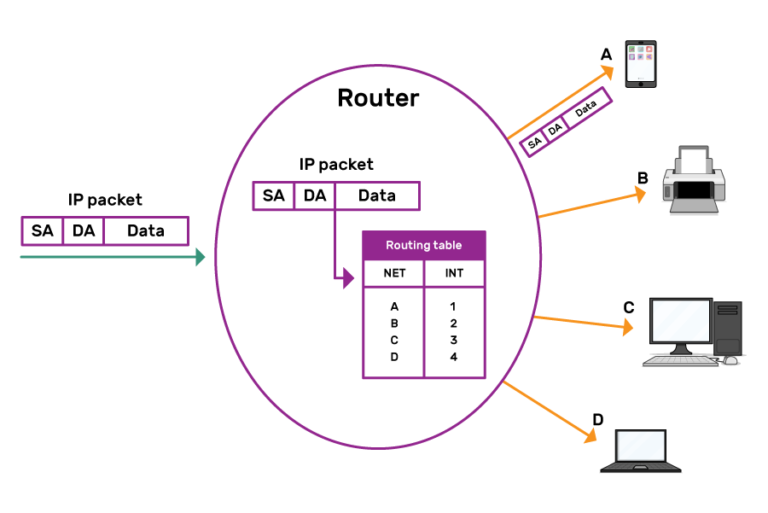
In the animation, an IP packet arrives at a router, which compares the parcel's destination address with the networks in the routing table. The package is identified as belonging to network A, so the router routes it out of interface 1.
Frequently, routers learn how to reach afar networks by exchanging data with their neighbouring routers and building their own routing tables. This exchange of data to acquire nearly other networks is chosen a routing protocol. You tin observe more than information about routing protocols on Wikipedia.
Note: the term 'routing protocol' can be easily confused with routed protocol. IP is a routed protocol: routers examine IP packets and route them out of an interface based on the destination IP address.
Routing on Dwelling house and Pocket-size Business Networks
A home or small-scale-business network commonly has a single LAN, which a router connects to an Internet service provider.
-
Each of the network's devices, including the actual interface on the router for the LAN, will have a 192.168.1.10 address. The internal LAN'southward network address is therefore 192.168.one.0.
-
The Router'south WAN interface has the accost 82.5.6.11, which is part of the ISP's 82.0.0.0 network.
So the router is continued to 2 dissimilar IP networks, which are automatically placed into the routing table. The default network, 0.0.0.0, gets configured so it sends data out via the WAN interface and onto the next router.
Bundle switching and circuit switching
Each router examines and sends each IP package individually — this is called packet switching. If the network changes, due to congestion or faults, routers can use an culling interfaces to accomplish a destination. So packets may travel over different routes to achieve the aforementioned destination.
Possible point of defoliation: despite the fact that this is chosen 'parcel switching', no switch devices are involved. Switches switch data frames betwixt ports, whereas routers route IP packets between interfaces.
Telephone systems use excursion switching: they send an initial packet to the destination, and along its path, this commencement packet reserves chapters on all of the links it uses. Information technology sets up a fixed route on each router specifically for this connection. This creates a guaranteed connectedness from end to end for the duration of the call. If capacity is unavailable, then no connexion is made and the system terminates the call.
The internet
The net is the interconnection of all the different networks that we accept discussed, and that people take created and are using in unlike capacities. For example:
- Domicile users with unmarried LANs
- Users around the world connecting to ISPs through smartphones
- Small and large companies with LANs and WANs
- Governments and ISPs with WANs that span the earth
ISPs interconnect with other ISPs, and this connects everything together into a gigantic WAN. This is the internet, which you'll learn more about adjacent week.
Information technology's estimated that virtually 50% of the earth'southward population has access to the internet.
Next up
In the next step, we'll show you how you tin can see the routers that your IP packets pass through on the manner to a web server.
Questions
- Can yous guess where fragmented IP packets are reassembled, and why that location?
- What do you think happens if a fragment of an IP packet fails to arrive?
- If a large corporation has multiple connections to the internet via dissimilar ISPs, how does information technology choose which way to transport traffic?
Join in the chat in the comments below to share your ideas.
Which Part Of The Ip Address Does The Router Use To Determine Where To Send Data Packets,
Source: https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/introduction-to-networking/0/steps/53448
Posted by: eskewbece1940.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Part Of The Ip Address Does The Router Use To Determine Where To Send Data Packets"
Post a Comment