What Are The Different Sizes Of Data
This is a lesson in the course Introduction to Computers, which is a part of The Schoolhouse of Computer Scientific discipline
This is a lesson in the course Computing Fundamentals
Names for different sizes of information [edit | edit source]
When choosing a new estimator we come up across terms such as "300GB hard bulldoze" and "500MB download", and to the uninitiated, this can be somewhat disconcerting. Data in a figurer is represented in a series of bits. Since the nativity of computers, bits accept been the language that control the processes that take identify inside that mysterious box called your estimator. In this commodity, nosotros look at the very language that your computer uses to do its work.
Bit [edit | edit source]
A bit is a binary unit, simply a 1 or a 0. A true or a simulated. It is the most basic unit of information in a computer. Information technology'due south like the dots and dashes in Morse code for a computer. Bits are motorcar readable.
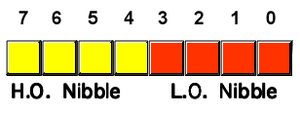
Nibble [edit | edit source]
A nibble is 4 bits, or half of a byte. One hexadecimal digit is one nibble in size.
Byte [edit | edit source]
In computer science a byte is a unit of measurement of information storage, that equals 'viii bits', can exist used to represent letters and numbers.
For instance, the number 01000001 is 8 $.25 long, and represents the letter A in viii-flake encoding.
Discussion [edit | edit source]
Unfortunately the term "discussion" has ii definitions.(i) The word size for a calculator is the number of bits that the central processing unit of measurement (CPU) of a particular computer can handle at i time. These word sizes range from a nibble to more than 128 bits. (ii) Word size = xvi bits (or ii bytes). This second definition was pretty much driven by all of the people that were writing software to exist used to program computers.
KB [edit | edit source]
A kilobyte, or KB, is a unit of data that equals 1024 bytes, or ii10. This is not to be confused with the decimal kilo which means g or xiii. The departure is considering the term was coined past calculator scientists. Powers of 2 do not fit into chiliad neatly, therefore using the decimal system in binary computing would be computationally wasteful.
MB [edit | edit source]
A megabyte, or MB, is a unit of information that equals 1,048,576 bytes, or 2xx. This is equal to a kilobyte squared, 10242.
GB [edit | edit source]

A gigabyte, or GB, is a unit of information that equals 1,073,741,824 bytes, or 230. This is equal to a kilobyte cubed, 1024three. Considering of the difference between computer metrics and decimal metrics, storage devices are usually advertised with gigabytes presented as 1 billion bytes rather than one.07 billion bytes, thereby understating their true capacity. This explains why there are inconsistencies when comparing the actual size of a hard drive to the presented size.
TB [edit | edit source]
A terabyte, or TB, is a unit of measurement of data that equals 1,099,511,627,776 bytes, or 240. This is equal to a kilobyte to the quaternary power, 10244, beingness approximately ane trillion bytes, or 1024 gigabytes. Consumer storage devices are often measured in terabytes.
PB [edit | edit source]

xiv petabytes stored within.
A petabyte, or Lead, is a unit of measurement of data that equals 1,125,899,906,842,624 bytes, or 250. This is equal to a kilobyte to the fifth ability, 10245, or roughly i quadrillion bytes. Large data centers, such as those operated by Google, can handle petabytes of data every day. Microsoft stores on 900 servers a total of approximately 14 petabytes. Cisco Systems predicts "the global Internet networks will evangelize 12.5 petabytes every 5 minutes in 2016."
Measurements of Information Speed [edit | edit source]

Data transfer speeds tin can be measured in $.25 per second, or in bytes per 2d. A byte is (by and large) 8 bits long. Network engineers depict network speeds in bits per second, while web browsers usually measure out a file download rate in bytes per 2nd. A lowercase "b" ordinarily ways a scrap, while an uppercase "B" represents a byte. In networking, metric prefixes (e.g. kilo, mega, and giga) refer to their decimal, not binary meaning.
bps [edit | edit source]
Known equally bits per second, bps was the main mode of describing data transfer speeds several decades agone.
Kbps [edit | edit source]
Kilobits per second, or chiliad bits per 2nd. The quality of compressed audio files (e.thou. MP3s) are typically measured in Kbps.
Mbps [edit | edit source]
Megabits per 2d, or 1,000,000 bits per 2d. Net service providers usually measure their Internet connectivity in Mbps.
Gbps [edit | edit source]
Gigabits per second, or i,000,000,000 bits per second. Modernistic local area networks, Cyberspace infrastructure, and consumer Internet connections in some countries can operate at these speeds.
What Are The Different Sizes Of Data,
Source: https://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Data_sizes_and_speeds
Posted by: eskewbece1940.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Are The Different Sizes Of Data"
Post a Comment